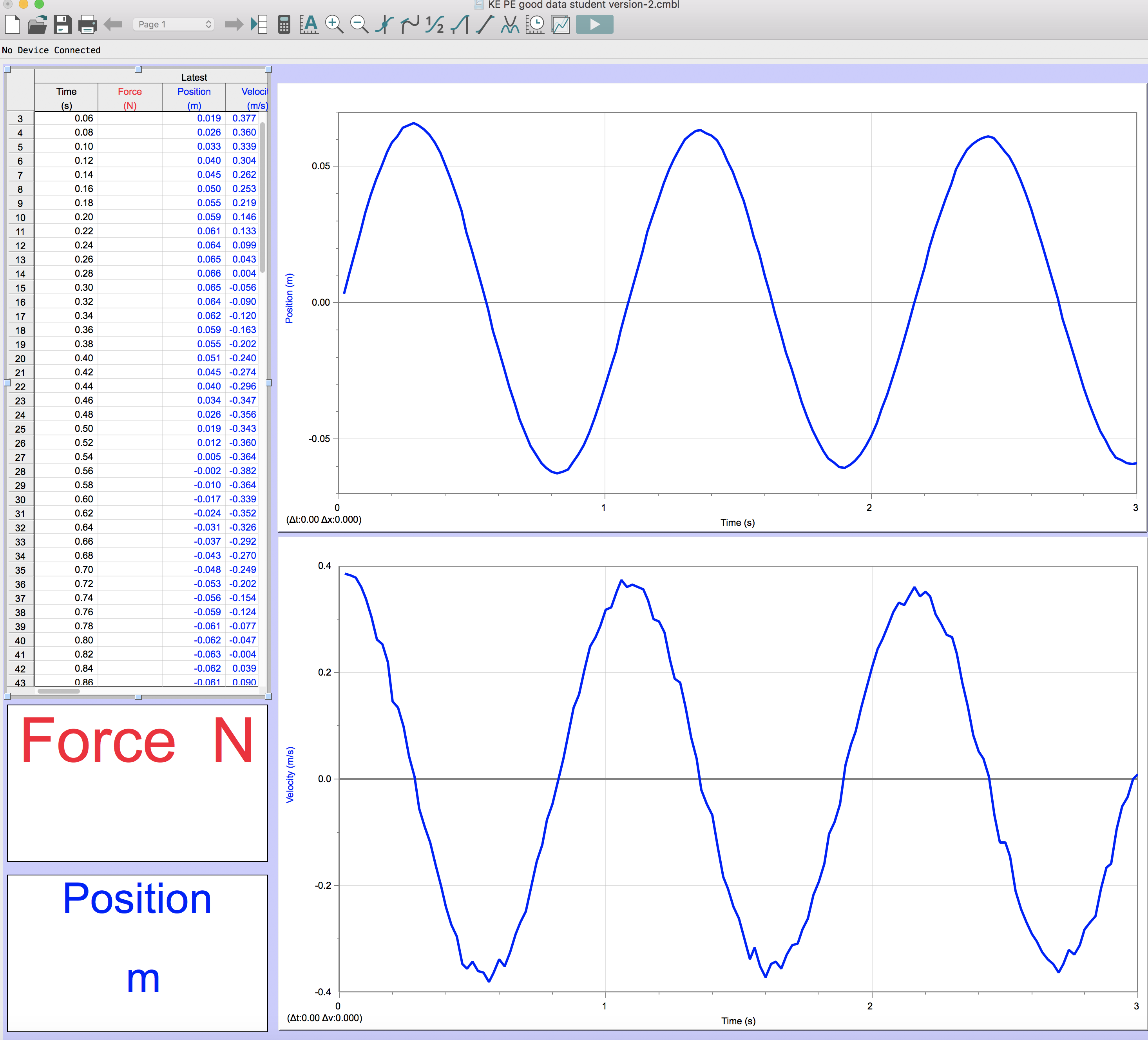
- Plot Short Story Example
- Plots Definition Math Example
- Dot Plots Definition
- Plots Definition Real Estate
countable a secret plan made by a group of people to do something wrong or illegal synonym conspiracy He had been the victim of an elaborate murder plot. Plot to do something The rebels hatched a plot to overthrow the government. Plot against somebody Police uncovered a plot against the president. Plot - a small area of ground covered by specific vegetation; 'a bean plot'; 'a cabbage patch'; 'a briar patch'. Plot of ground, plot of land, patch. Bed - a plot of ground in which plants are growing; 'the gardener planted a bed of roses'. Garden - a plot of ground where plants are cultivated.

Plot y versus x as lines and/or markers.
Call signatures:
The coordinates of the points or line nodes are given by x, y.
Plot y versus x as lines and/or markers.
Call signatures:
The coordinates of the points or line nodes are given by x, y.
The optional parameter fmt is a convenient way for defining basicformatting like color, marker and linestyle. It's a shortcut stringnotation described in the Notes section below.
You can use Line2D properties as keyword arguments for morecontrol on the appearance. Line properties and fmt can be mixed.The following two calls yield identical results:
When conflicting with fmt, keyword arguments take precedence.
Plotting labelled data
There's a convenient way for plotting objects with labelled data (i.e.data that can be accessed by index obj['y']). Instead of givingthe data in x and y, you can provide the object in the dataparameter and just give the labels for x and y:
All indexable objects are supported. This could e.g. be a dict, apandas.DataFame or a structured numpy array.
Plotting multiple sets of data
There are various ways to plot multiple sets of data.
The most straight forward way is just to call
plotmultiple times.Example:Alternatively, if your data is already a 2d array, you can pass itdirectly to x, y. A separate data set will be drawn for everycolumn.
Example: an array
awhere the first column represents the xvalues and the other columns are the y columns:The third way is to specify multiple sets of [x], y, [fmt]groups:
In this case, any additional keyword argument applies to alldatasets. Also this syntax cannot be combined with the dataparameter.
By default, each line is assigned a different style specified by a'style cycle'. The fmt and line property parameters are onlynecessary if you want explicit deviations from these defaults.Alternatively, you can also change the style cycle usingrcParams['axes.prop_cycle'] (default: cycler('color', ['#1f77b4', '#ff7f0e', '#2ca02c', '#d62728', '#9467bd', '#8c564b', '#e377c2', '#7f7f7f', '#bcbd22', '#17becf'])).
| Parameters: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Returns: |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other Parameters: |
|
See also
scatter- XY scatter plot with markers of varying size and/or color ( sometimes also called bubble chart).
Notes
Format Strings
A format string consists of a part for color, marker and line:
Each of them is optional. If not provided, the value from the stylecycle is used. Exception: If line is given, but no marker,the data will be a line without markers.
Other combinations such as [color][marker][line] are alsosupported, but note that their parsing may be ambiguous.
Markers
| character | description |
|---|---|
'.' | point marker |
',' | pixel marker |
'o' | circle marker |
'v' | triangle_down marker |
'^' | triangle_up marker |
'<' | triangle_left marker |
'>' | triangle_right marker |
'1' | tri_down marker |
'2' | tri_up marker |
'3' | tri_left marker |
'4' | tri_right marker |
's' | square marker |
'p' | pentagon marker |
'*' | star marker |
'h' | hexagon1 marker |
'H' | hexagon2 marker |
'+' | plus marker |
'x' | x marker |
'D' | diamond marker |
'd' | thin_diamond marker |
'|' | vline marker |
'_' | hline marker |
Line Styles
| character | description |
|---|---|
'-' | solid line style |
'--' | dashed line style |
'-.' | dash-dot line style |
':' | dotted line style |
Example format strings:
Colors
The supported color abbreviations are the single letter codes
| character | color |
|---|---|
'b' | blue |
'g' | green |
'r' | red |
'c' | cyan |
'm' | magenta |
'y' | yellow |
'k' | black |
'w' | white |
and the 'CN' colors that index into the default property cycle.
Plot Short Story Example
If the color is the only part of the format string, you canadditionally use any matplotlib.colors spec, e.g. full names('green') or hex strings ('#008000').
Also called: box plot, box and whisker diagram, box and whisker plot with outliers
A box and whisker plot is defined as a graphical method of displaying variation in a set of data.In most cases, a histogram analysis provides a sufficient display, but a box and whiskerplot can provide additional detail while allowing multiple sets of data to be displayed in the same graph.
Why Use a Box and Whisker Plot?
Box and whisker plots are very effective and easy to read, as they can summarize datafrom multiple sources and display the results in a single graph. Box and whiskerplots allow for comparison of data from different categories for easier, more effectivedecision-making.
When to Use a Box and Whisker Plot
Use box and whisker plots when you have multiple data sets from independentsources that are related to each other in some way. Examples include:
- Test scores between schools or classrooms
- Data from before and after a process change
- Similar features on one part, such as camshaft lobes
- Data from duplicate machines manufacturing the same products
How to Make a Box and Whisker Plot
The procedure to develop a box and whisker plot comes from the five statistics below. You can also download the box and whisker plot template.
- Minimum value: The smallest value in the data set
- Second quartile: The value below which the lower 25% of the data are contained
- Median value: The middle number in a range of numbers
- Third quartile: The value above which the upper 25% of the data are contained
- Maximum value: The largest value in the data set
For example, given the following 20 data points, the five required statistics are displayed.
| Number | Data | |
| 1 | 113 | Minimum value: 113 |
| 2 | 116 | |
| 3 | 119 | |
| 4 | 121 | |
| 5 | 124 | |
| 2nd quartile: 124 | ||
| 6 | 124 | |
| 7 | 125 | |
| 8 | 126 | |
| 9 | 126 | |
| 10 | 126 | |
| Median value: 126.5 | ||
| 11 | 127 | |
| 12 | 127 | |
| 13 | 128 | |
| 14 | 129 | |
| 15 | 130 | |
| 3rd quartile: 130 | ||
| 16 | 130 | |
| 17 | 131 | |
| 18 | 132 | |
| 19 | 133 | |
| 20 | 136 | Maximum value: 136 |
Note: For a data set with an even number of values, the median is calculated as the average of the two middle values.
The data represented in box and whisker plot format can be seen in Figure 1.
Figure 1 Box and Whisker Plot Example
Left figure: The center represents the middle 50%, or 50th percentile of the data set, and is derived using the lower and upper quartile values. The median value is displayed inside the 'box.' The maximum and minimum values are displayed with vertical lines ('whiskers') connecting the points to the center box.
Right figure: For comparison, a histogram of the data is also shown, showing the frequency of each value in the data set.
Box and Whisker Plot Example
Plots Definition Math Example
Suppose you wanted to compare the performance of three lathes responsible for the rough turning of a motor shaft. The design specification is 18.85 +/- 0.1 mm.
Yucasin sigma aldrich. Diameter measurements from a sample of shafts taken from each roughing lathe are displayed in a box and whisker plot in Figure 2.
Dot Plots Definition
Figure 2 Box and Whisker Plot Lathe Comparison Example
- Lathe 1 appears to be making good parts, and is centered in the tolerance.
- Lathe 2 appears to have excess variation, and is making shafts below the minimum diameter.
- Lathe 3 is performing with relatively less variation than Lathe 2; however, it is centered on the lower side of the specification and is making shafts below specification.
